es作为 db、搜索、alap以及成熟的社区,已经越来越成为后端比较成熟的技术栈了,业务中由于需要大量聚合操作,来弥补传统关系型数据(My-SQL)的性能不足,行数据库的劣势,往往会以es作为辅助的存储工具,因此深入学习es基本概念,原理对于日常开发有很大的帮助!对于SQL-Body来说,es支持SQL语法,还是相当给力的!
由于我们公司es集群基本使用的是 6.8.8版本,所以全部学习资料基于这个版本学习!
1、官方文档
6.8版本的官方文档,推荐大家学习的时候详细阅读一下!! , 中文版可能只有2.x版本的!
2、docker安装ES环境
这里不去做集群节点,本文只是做练习,所以不去搭建那么多节点!(docker是个好工具,对于本地学习软件)
1
2
3
4
5
6
| # 创建bridge网络
docker network create elasticsearch
# 创建es(signle-node)
docker run -d --rm --name elasticsearch -p 9200:9200 -p 9300:9300 --network elasticsearch -e "discovery.type=single-node" elasticsearch:6.8.8
# 创建kibana(web-console)
docker run -d --rm --name kibana -p 5601:5601 --network elasticsearch kibana:6.8.8
|
3、相关概念
1、索引
elastic-search 的基本概念: 索引(index) -> type(类型) -> document(文档) -> field (字段) 和关系型数据库的关系如下:
- Relational DB -> Databases -> Tables -> Rows -> Columns
- Elasticsearch -> Indices -> Types -> Documents -> Fields
但是其实开发上实际上不允许一个索引创建多个类型的,所以也就是为什么后期es废弃了type,最终到8.X版本废弃掉了!原因其实根据es底层有关,影响检索效率,这个和es存储于Lucene 的关系了
在6.x版本只支持一个索引一个type,在7.x版本移除了 type ,8.x彻底废弃,主要原因还是因为lucene的底层设置问题,可以看一下官方文档:https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/6.8/removal-of-types.html
如何创建一个索引呢
首先先要pass掉那种直接插入数据进行创建索引的,对于线上业务来说不允许开发者去以这种方式去创建索引的,es可以做控制!其次就是创建索引6.x版本后只能创建一个type,推荐type设置为 _doc,其次就是指定属性了
这个例子是创建一个my_index索引,然后创建一个_doc 类型,字段是 full_name,类型为 text
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| PUT my_index
{
"mappings": {
"_doc": {
"properties": {# 属性
"full_name": { # 字段名称
"type": "text" # 字段属性控制,具体根据官方配置走
}
}
}
}
}
|
关于更多索引的配置可以参考:mapping字段类型 和 mapping 的字段参数
核心关注的几个点吧,1、字段的类型 type,2、字段是否可以被索引(默认true)由index控制,3、字段的分词器 analyzer,4、fields 属性(text类型特有的)
索引的类型使用就不介绍了,这个根据经验有关,主要有基本类型,数组,对象,geo,
以日志收集来说
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
| {
"filebeat-xxxxxxx-2021.03.11": {
"mappings": {
"doc": {
"properties": {
"@timestamp": {
"type": "date"
},
"agent": {
"type": "object"
},
"ecs": {
"type": "object"
},
"fields": {
"properties": {
"log_type": {
"type": "text",
"fields": {
"keyword": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 256
}
}
}
}
},
"host": {
"properties": {
"name": {
"type": "text",
"fields": {
"keyword": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 256
}
}
}
}
},
"input": {
"type": "object"
},
"log": {
"properties": {
"file": {
"type": "object"
}
}
},
"message": {
"type": "text",
"fields": {
"keyword": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 256
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
|
数据:
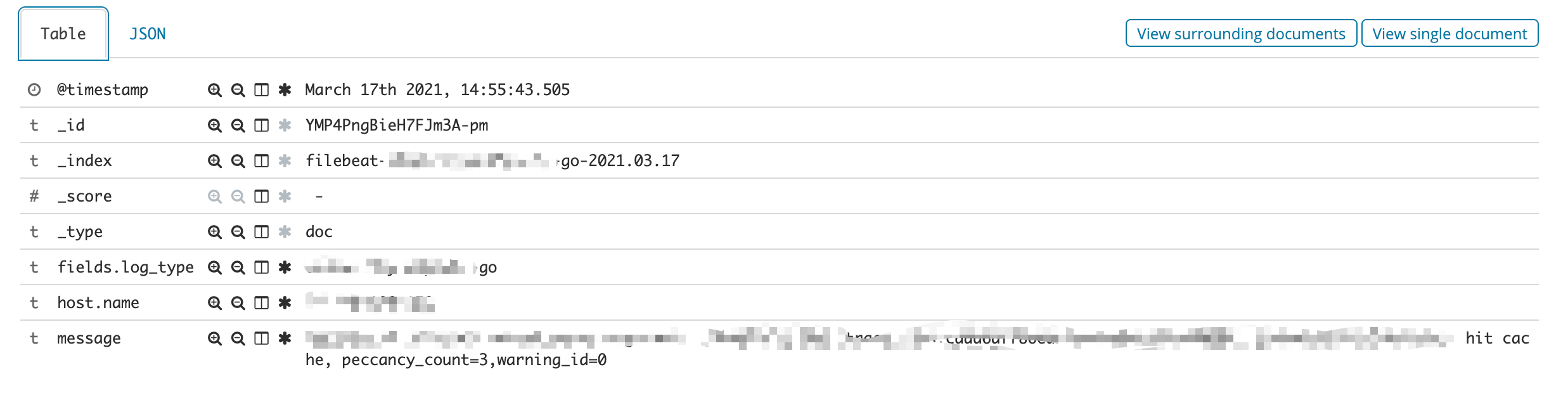
2、字段
业务中通常关注的是字段设置,因为字段关系到你的数据结构设计,掌握好es的数据结构很重要,下面这个例子我会大概展示如何设置一个结构体
复杂对象如何存储/检索
1、存储主要是采用json的扁平化
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| PUT my_index/_doc/1
{
"region": "US",
"manager": {
"age": 30,
"name": {
"first": "John",
"last": "Smith"
}
}
}
|
=> 存储到es中由于Lucene没有对象检索这种概念,所以会进行扁平化存储
1
2
3
4
5
6
| {
"region": "US",
"manager.age": 30,
"manager.name.first": "John",
"manager.name.last": "Smith"
}
|
2、检索的话和普通字段基本就没有差异了,只要准寻扁平化字段进行检索
参考:https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/6.8/object.html
对象数组如何存储/检索
es里面叫做 nested ,中文名称叫做嵌套
类似于下面的数组,对于es来说,到底是怎么存储的呢???
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| PUT my_index/_doc/1
{
"group" : "fans",
"user" : [
{
"first" : "John",
"last" : "Smith"
},
{
"first" : "Alice",
"last" : "White"
}
]
}
|
es会将其存储为
1
2
3
4
5
| {
"group" : "fans",
"user.first" : [ "alice", "john" ],
"user.last" : [ "smith", "white" ]
}
|
因为这里就会有个问题了,那么我查询咋查哇,如何确定唯一,比如查询Alice-Smith,但是其实查询出内容
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| GET my_index/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{ "match": { "user.first": "Alice" }},
{ "match": { "user.last": "Smith" }}
]
}
}
}
|
fields 字段的作用
是我基于官方文档对于这个概念的理解,文档: https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/6.8/multi-fields.html
功能一:聚合
1、加入要做keyword了,比如说你的日志可能分类型记录,比如请求超时,请求无权限,请求参数错误,对于这种简单的参数进行聚合统计,但是由于日志需要做全文检索,所以不能设置为 keyword,这里就使用 fields !
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
| DELETE /my_index
PUT /my_index
{
"settings": {
"number_of_replicas": 1,
"number_of_shards": 5
},
"mappings":{
"_doc":{
"properties":{
"message":{
"type":"text",
"fields":{
"keyword": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 10
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
POST /my_index/_doc
{
"message":"请求超时"
}
POST /my_index/_doc
{
"message":"业务日志:name: xiaoli, id: 111"
}
POST /my_index/_doc
{
"message":"请求无权限"
}
POST /my_index/_doc
{
"message":"请求参数错误"
}
|
2、进行检索:
2.1、使用kibana会自动告诉你keywork,进行聚合统计
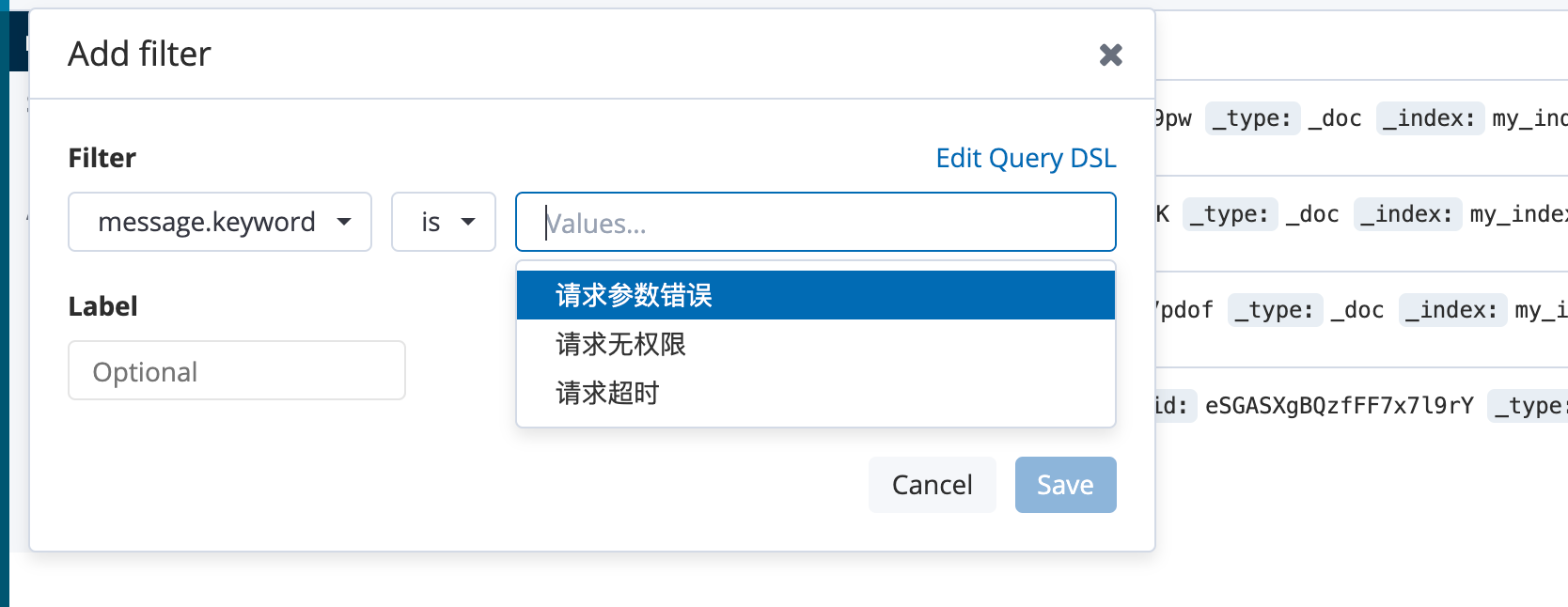
2.2、我还可以通过日志进行全文检索
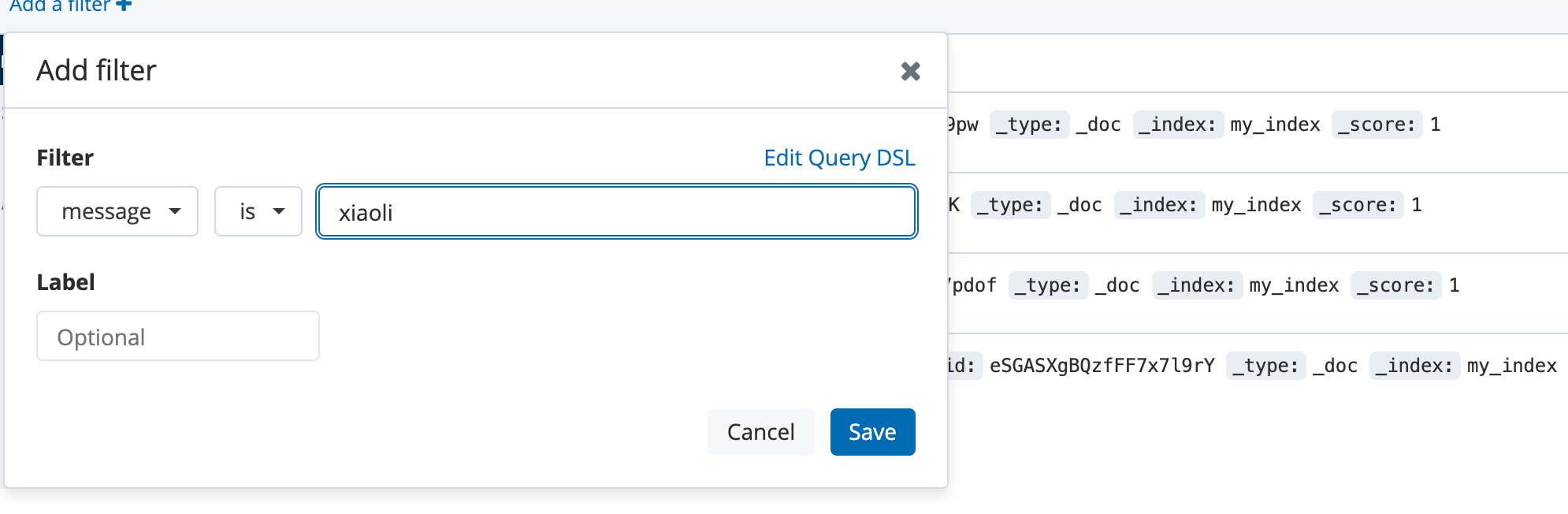
3、但是对于es来说,如果你没有指定mapping去创建一个索引,
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| POST /test_index/_doc
{
"message":"hello"
}
GET /test_index/_mapping
{
"test_index" : {
"mappings" : {
"_doc" : {
"properties" : {
"message" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
|
可以看到对于 text类型,默认会支持 256个字符的keyword,聚合检索
功能二:分词
业务上一个字段可能使用多种分词,这里就支持分词属性
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| PUT my_index
{
"mappings": {
"_doc": {
"properties": {
"text": {
"type": "text",
"fields": {
"english": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "english"
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
|
3、相关操作
1、插入
megacorp 表示index,employee 表示类型,3表示id-document
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| PUT /megacorp/employee/3
{
"first_name": "Douglas",
"last_name": "Fir",
"age": 35,
"about": "I like to build cabinets",
"interests": [
"forestry"
]
}
|
2、查询
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| GET /megacorp/employee/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"first_name": "Anthony"
}
}
}
|
3、过滤查询
过滤查询已被弃用,并在ES 5.0中删除。现在应该使用bool / must / filter查询。
4、更新
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| POST /megacorp/employee/3/_update
{
"doc":{
"age":22,
"deatil":"my name is ...."
}
}
|
加入添加一个字段,但是这个索引的mapping不变
健康状态:
Elasticsearch 集群和索引健康状态及常见错误说明