学习docker的基本组件、dockerfile、docker命令等!
官方文章:https://docs.docker.com/
docker 官方镜像地址: https://hub.docker.com/
推荐阅读丛书 : Docker实战(博文视点出品) 第一本Docker书 修订版
docker 快速安装: curl -fsSL https://get.docker.com | bash -s docker --mirror Aliyun , 记得用户设置在docker用户组!,推荐在非mac os/windows上玩。
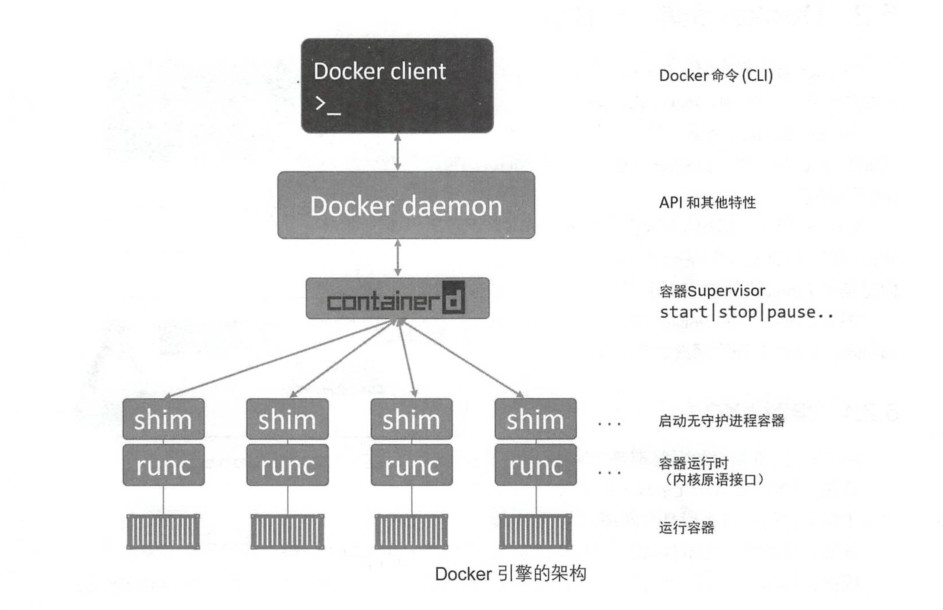
1、docker 的组成
1、runc runc实质上是一个轻量级的、针对Libcontainer进行了包装的命令 行交互工具( Libcontainer取代了早期Docker架构中的LXC )。
使用很简单,它是运行一个容器最基本的工具,所以我们需要创建容器。
docker中创建容器是,docker create docker-image-name,但是需要导出到文件系统中
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 # create the top most bundle directory mkdir /mycontainer cd /mycontainer # create the rootfs directory mkdir rootfs # export busybox via Docker into the rootfs directory docker export $(docker create busybox) | tar -C rootfs -xvf - runc spec # run as root cd /mycontainer runc run mycontainerid
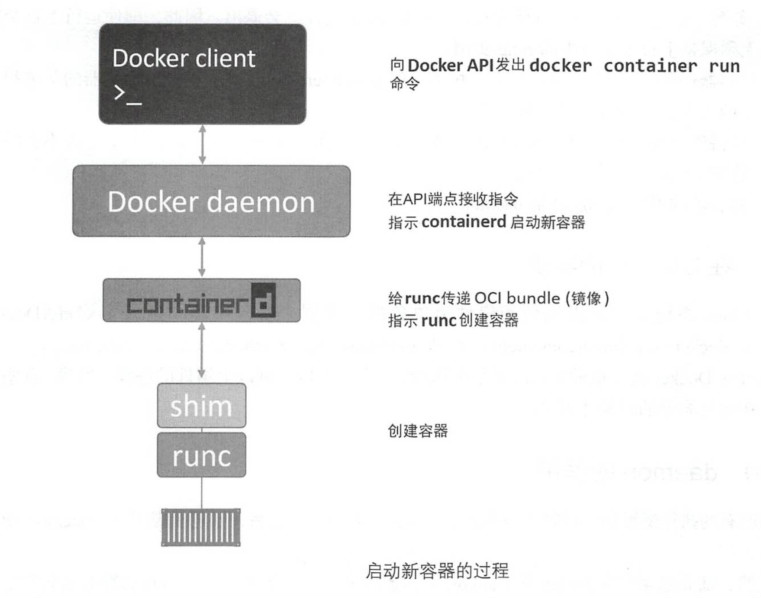
2、containerd 对于docker进行拆分后,容器执行逻辑被重构到一个新的名为containerd (发音为container-dee) 的工具中。它的主要任务是容器的生命周期管理———— start | stop | pause | rm….
Docker引擎技术栈中,containerd位于daemon和runc所在的OCI层之间。随着时间的推移,它被赋予了更多的功能,如镜像管理。虽然名叫containerd, 但是它并不负责创建容器,而是指挥runc去做。containerd将Docker镜像转换为OCI bundle,并让runc基于此创建一个新的容器。然后,runc与操作系统内核接口进行通信,基于所有必要的工具( Namespace、CGroup 等)来创建容器。容器进程作为runc的子进程启动,启动完毕后,runc 将会退出。
将所有的用于启动、管理容器的逻辑和代码从daemon中移除,意味着容器运行时与Docker daemon是解耦的,有时称之为“无守护进程的容器(daemonless container)”,如此,对Docker daemon的维护和升级工作不会影响到运行中的容器。
3、shim shim是实现无daemon的容器(用于将运行中的容器与daemon解耦,以便进行daemon升级等操作)不可或缺的工具。containerd 指挥runc来创建新容器。事实上,每次创建容器时它都会fork一个新的runc实例。不过,一旦容器创建完毕,对应的runc进程就会退出。因此,即使运行上百个容器,也无须保持上百个运行中的runc实例。一旦容器进程的父进程runc退出,相关联的containerd-shim 进程就会成为容器的父进程。
作为容器的父进程,shim 的部分职责如下。
保持所有STDIN和STDOUT流是开启状态,从而当daemon重启的时候,容器不会因为管道( pipe)的关闭而终止。 将容器的退出状态反馈给daemon。 4、daemon daemon的主要功能包括镜像管理、镜像构建、REST API、身份验证、安全、核心网络以及编排。
2、Dockerfile 学习 官方文档: https://docs.docker.com/engine/reference/builder/
1、dockerfile 文件,基本玩法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 FROM alpine:latestMAINTAINER anthony-dong "fanhaodong516@gamil.com" RUN mkdir -p /opt/project WORKDIR /opt/project ADD project.tar.gz . COPY run.sh . EXPOSE 8080 VOLUME [ "/opt/project" ] ENV PROJECT_HOME /opt/projectENV PATH $PATH:$PROJECT_HOMECMD ["/bin/sh" ,"-c" ,"run.sh" ]
执行:
1 2 3 docker build -t test . docker run --rm -it test
2、CMD 和 ENTRYPOINT 的区别 CMD 和 ENTRYPOINT 的区别,这里其实区别很简单, 可以理解为 在没有启动命令是 ENTRYPOINT+ CMD (启动docker run时运行的默认命令)当我们 docker run image_name [cmd1] [cmd2] 时,其实已经把 Dokerfile中配置的CMD命令替换掉了,其实真正执行的是 ENTRYPOINT+[cmd1]+[cmd2] , 但是这俩CMD 和 ENTRYPOINT 都可以为空 根据上面可以发现 CMD可以通过 docker run可以替换,那么 ENTRYPOINT 也是可以替换的,可以通过 -entrypoint 指定 1 2 3 FROM alpine:latest ENTRYPOINT [ "ls" ] CMD ["-al" ]
比如上面找个,我们如果默认执行的话,会是:
1 2 3 4 5 6 ➜ kubernetes docker run --rm demo total 64 drwxr-xr-x 1 root root 4096 Jan 26 12:50 . // ... drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Jan 14 11:49 opt dr-xr-xr-x 226 root root 0 Jan 26 12:50 proc
但是如果我们添加了参数:
1 2 3 4 5 6 ➜ kubernetes docker run --rm demo -a .. .dockerenv bin //.... home
修改 ENTRYPOINT
1 2 3 4 ➜ kubernetes docker run --rm --entrypoint env demo PATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin HOSTNAME=4791 b485ab53 HOME=/root
3、AND 和 COPY的区别 AND 可以是多种source源,支持url/tar/unzip/文件包,所以看需求选择,比如使用tar包会自动解压
COPY 只能copy文件,所以一般推荐copy
4、build 失败如何继续,如何调试!! 1 2 3 FROM centos:centos7USER admin:adminCMD [ "/bin/bash" ]
这个build是可以通过的!!!
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 ➜ docker-file-test docker build -t test-1 . Sending build context to Docker daemon 25.09kB Step 1/3 : FROM centos:centos7 ---> 7e6257c9f8d8 Step 2/3 : USER admin:admin ---> Running in f8ed46bdda32 Removing intermediate container f8ed46bdda32 ---> 9611a153742e Step 3/3 : CMD [ "/bin/bash" ] ---> Running in abc32bd8e245 Removing intermediate container abc32bd8e245 ---> 0f0f0aeeec29 Successfully built 0f0f0aeeec29 Successfully tagged test-1:latest
然后运行
1 2 ➜ docker-file-test docker run --rm -it test-1 docker: Error response from daemon: linux spec user: unable to find user admin: no matching entries in passwd file.
发现这个,我们需要从Step 1/3开始!!!
1 2 3 4 5 ➜ docker-file-test docker run --rm -it 7e6257c9f8d8 [root@532c8a693273 /]# useradd admin -p admin -d /home/admin --create-home -s /bin/bash [root@532c8a693273 /]# su admin [admin@532c8a693273 /]$ exit exit
然后我们需要继续改dockerfile
1 2 3 4 FROM centos:centos7 RUN useradd admin -p admin -d /home/admin --create-home -s /bin/bash USER admin:admin CMD [ "/bin/bash" ]
继续运行
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 ➜ docker-file-test docker build -t test-1 . Sending build context to Docker daemon 25.09kB Step 1/4 : FROM centos:centos7 ---> 7e6257c9f8d8 Step 2/4 : RUN useradd admin -p admin -d /home/admin --create-home -s /bin/bash ---> Running in f36f10b603bd Removing intermediate container f36f10b603bd ---> 843554e160f7 Step 3/4 : USER admin:admin ---> Running in 796341a1be27 Removing intermediate container 796341a1be27 ---> ab964ed78d8f Step 4/4 : CMD [ "/bin/bash" ] ---> Running in 2c67de0242ea Removing intermediate container 2c67de0242ea ---> 17a4bc8d7206 Successfully built 17a4bc8d7206 Successfully tagged test-1:latest ➜ docker-file-test docker run --rm -it 17a4bc8d7206 [admin@55f84f22acf6 /]$
这个就是一个简单的过程!!!!!!,这个好处是类似于调试的过程
其实还可以通过 docker run -u 来制定用户,切记一点,别记忆命令!!,要记忆如何学习!!
1 2 ➜ docker-file-test docker run -it --rm --user root test-1 [root@6dbeb01f5329 /]#
5、安装一个Go的环境 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 FROM centos:centos7MAINTAINER anthony-dong "fanhaodong516@gamil.com" ADD go1.13.15.linux-amd64.tar.gz /opt RUN mkdir /opt/project \ && yum install -y vim \ && yum install -y curl \ && yum install -y git \ && yum install -y wget ENV GO_HOME "/opt/go" ENV PATH $PATH:$GO_HOME/binEXPOSE 8080 EXPOSE 10010 CMD [ "/bin/bash" ]
然后执行, --tag 可以写成-t ,比如--tag go:1.13 意思就是镜像名称是go,版本是1.13,大致就是这个样子!
1 docker build --file ./Dockerfile -p --tag goenv1.13 .
最后启动需要指定-t ,意思就是 --rm是容器被停止则被删除,-d是deamon启动, -it就是hold住类似于开启一个终端(i是输出,t是终端,然后程序就被hold住了), -P暴漏端口随机到宿主机上, 最后指定使用的镜像
1 docker run --rm -d -it -P goenv1.13
然后查看一下
1 2 3 ➜ test docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES f67a0f2bcb0e goenv1.13 "/bin/bash" 21 seconds ago Up 19 seconds 0.0.0.0:32769->8080/tcp, 0.0.0.0:32768->10010/tcp heuristic_lumiere
6、多阶段构建 Docker v17.05 开始支持多阶段构建 (multistage builds), 参考:https://yeasy.gitbook.io/docker_practice/image/multistage-builds , 主要命令就是 COPY --from=builder /data/apps/project/bin/app bin/
但是业务中不推荐,很多时候要去容器里操作!
还是一个Go项目,假如以一个Http-Server 为例子
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 ➜ pck tree -L 2 . ├── Dockerfile ├── cmd │ └── main.go ├── go.mod └── go.sum
项目文件:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 package main import ( "github.com/gin-gonic/gin" "log" "net/http" ) func main() { router := gin.Default() router.GET("/echo", func(context *gin.Context) { context.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{ "code": 0, "data": "hello world", "message": "success", }) }) log.Fatal(router.Run(":8080")) }
Dockerfile
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 # 1.11+ 默认自动支持Go mod,切记builder的编译和运行的编译内核一致 FROM golang:1.13.15-alpine3.12 as builder # 全局变量,项目名称 ARG GOPROXY=https://goproxy.cn,direct ENV GOPROXY=${GOPROXY} WORKDIR /data COPY . . RUN go build -v -ldflags "-s -w" -o bin/app cmd/main.go FROM alpine:3.12 as runing # 切记环境变量不能共享 ARG PROJECT_NAME=project ARG PROJECT_PORT=8080 WORKDIR /data/${PROJECT_NAME} COPY . . # 含义是 copy上一个镜像的 /data/${PROJECT_NAME} /bin/app 文件到当前目录的bin COPY --from=builder /data/bin/app bin/ # COPY --from=0 /opt/bin/app . EXPOSE ${PROJECT_PORT} CMD [ "bin/app" ]
编译 :(注意 alpine是不支持 race 的,会编译报错)
启动:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 ➜ my-docker docker run --rm -p 8080:8080 test [GIN-debug] [WARNING] Creating an Engine instance with the Logger and Recovery middleware already attached. [GIN-debug] [WARNING] Running in "debug" mode. Switch to "release" mode in production. - using env: export GIN_MODE=release - using code: gin.SetMode(gin.ReleaseMode) [GIN-debug] GET /echo --> main.main.func1 (3 handlers) [GIN-debug] Listening and serving HTTP on :8080
查看大小:
1 2 3 4 ➜ my-docker docker images REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE test latest fdbca700806f 8 minutes ago 17.8MB alpine latest 7731472c3f2a 6 days ago 5.61MB
其实真实的Go的构建不是这种,一般都有打包机器,无须我们去找机器编译和运行
7、构建多种系统架构支持的 Docker 镜像 https://yeasy.gitbook.io/docker_practice/image/manifest
3、Docker 限制资源 压测程序,不准确,因为数组扩容,是十分消耗内存的,如果内存满了,无法申请内存,那么就不会打印消息!可以使用stress工具来测试CPU和内存。这里我也懒得下载!!
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 package mainimport ( "fmt" "os" "strconv" "time" ) var ( ref []byte ) func main () fmt.Println(os.Getpid()) mem, _ := strconv.ParseInt(os.Args[1 ], 10 , 64 ) for { if mem == 0 { mem = 1 } size := 1024 * 1024 * mem newSlice(size) time.Sleep(time.Second) } } func newSlice (size int64 ) add := make ([]byte , size) ref = append (ref, add...) fmt.Println(fmt.Sprintf("%s %v\n" , time.Now().Format("15:04:05" ), os.Getpid())) }
下面表示:表示在现在的内存是200M,cpu限制是1
1 ➜ go-demo docker run -it --rm --memory 200M --cpuset-cpus="1" --oom-kill-disable -v /Users/dong/go/version/go-1.13.5:/opt/project ce2534430fc2 /bin/bash
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 [root@17d356297d5f project]# go build -o bin/main study/slice/main2.go // .. 可以发现在45s的卡壳了,也就是内存被限制了 08:52:44 103 08:52:45 103 top - 08:52:45 up 5:24, 0 users, load average: 0.96, 1.45, 1.12 Tasks: 4 total, 1 running, 3 sleeping, 0 stopped, 0 zombie % Cpu(s): 0.3 us, 3.0 sy, 0.0 ni, 93.3 id, 1.0 wa, 0.0 hi, 2.4 si, 0.0 st KiB Mem : 2046748 total, 1592784 free, 324656 used, 129308 buff/cache// 这些信息是假的,不能看 KiB Swap: 1048572 total, 703508 free, 345064 used. 1582140 avail Mem PID USER PR NI VIRT RES SHR S %CPU %MEM TIME+ COMMAND 103 root 20 0 645568 200120 68 S 18.9 9.8 0:01.31 main // 200 m 1 root 20 0 11836 2400 2400 S 0.0 0.1 0:00.15 bash 51 root 20 0 11836 2332 2332 S 0.0 0.1 0:00.05 bash 71 root 20 0 56188 2016 1924 R 0.0 0.1 0:00.03 top
查看docker容器真实的内存,可以
1 2 3 ➜ ~ docker stats 17d356297d5f CONTAINER ID NAME CPU % MEM USAGE / LIMIT MEM % NET I/O BLOCK I/O PIDS 17d356297d5f cocky_shaw 0.00% 199.4MiB / 200MiB 99.69% 1.18kB / 0B 357MB / 927MB 7
1、关于内存设置这几个参数的关系 选项 描述 -m,--memory内存限制,格式是数字加单位,单位可以为 b,k,m,g。最小为 4M --memory-swap内存+交换分区大小总限制。格式同上。必须必-m设置的大 --memory-reservation内存的软性限制。格式同上 --oom-kill-disable是否阻止 OOM killer 杀死容器,默认没设置 --oom-score-adj容器被 OOM killer 杀死的优先级,范围是[-1000, 1000],默认为 0 --memory-swappiness用于设置容器的虚拟内存控制行为。值为 0~100 之间的整数 --kernel-memory核心内存限制。格式同上,最小为 4M
–memory-swap 值必须比**–memory** 值大,因为:–memory-swap不是交换分区,而是内存加交换分区的总大小
1. 不设置 如果不设置-m,–memory和–memory-swap,容器默认可以用完宿舍机的所有内存和 swap 分区。不过注意,如果容器占用宿主机的所有内存和 swap 分区超过一段时间后,会被宿主机系统杀死(如果没有设置–00m-kill-disable=true的话)。
2. 设置-m,–memory,不设置–memory-swap 给-m或–memory设置一个不小于 4M 的值,假设为 a,不设置–memory-swap,或将–memory-swap设置为 0。这种情况下,容器能使用的内存大小为 a,能使用的交换分区大小也为 a。因为 Docker 默认容器交换分区的大小和内存相同。
如果在容器中运行一个一直不停申请内存的程序,你会观察到该程序最终能占用的内存大小为 2a。
比如$ docker run -m 1G ubuntu:16.04,该容器能使用的内存大小为 1G,能使用的 swap 分区大小也为 1G。容器内的进程能申请到的总内存大小为 2G。
3. 设置-m,–memory=a,–memory-swap=b,且b > a 给-m设置一个参数 a,给–memory-swap设置一个参数 b。a 时容器能使用的内存大小,b是容器能使用的 内存大小 + swap 分区大小。所以 b 必须大于 a。b -a 即为容器能使用的 swap 分区大小。
比如$ docker run -m 1G –memory-swap 3G ubuntu:16.04,该容器能使用的内存大小为 1G,能使用的 swap 分区大小为 2G。容器内的进程能申请到的总内存大小为 3G。
4. 设置-m,–memory=a,–memory-swap=-1 给-m参数设置一个正常值,而给–memory-swap设置成 -1。这种情况表示限制容器能使用的内存大小为 a,而不限制容器能使用的 swap 分区大小。
这时候,容器内进程能申请到的内存大小为 a + 宿主机的 swap 大小。
2、cpu限制 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 ➜ ~ docker run --help Usage: docker run [OPTIONS] IMAGE [COMMAND] [ARG...] Run a command in a new container Options: --add-host list Add a custom host-to-IP mapping (host:ip) -c, --cpu-shares int CPU shares (relative weight) --cpus decimal Number of CPUs --cpuset-cpus string CPUs in which to allow execution (0-3, 0,1) --cpuset-mems string MEMs in which to allow execution (0-3, 0,1)
选项 描述 --cpuset-cpus=""允许使用的 CPU 集,值可以为 0-3,0,1 -c,--cpu-shares=0CPU 共享权值(相对权重) cpu-period=0限制 CPU CFS 的周期,范围从 100ms~1s,即[1000, 1000000] --cpu-quota=0限制 CPU CFS 配额,必须不小于1ms,即 >= 1000 --cpuset-mems=""允许在上执行的内存节点(MEMs),只对 NUMA 系统有效
关于CFS的概念: https://www.jianshu.com/p/1da5cfd5cee4
后端基本不需要关注cpu,因为本身不是cpu密集型业务,基本都是io密集型/内存密集型。
4、docker push 命令 输入姓名,输入密码
1 2 3 docker images go1.13.15 latest ce2534430fc2 26 minutes ago 769MB
一般是 : docker tag <镜像名称> <用户名>/<镜像名称>:<镜像版本号>
1 docker tag go1.13.15 fanhaodong/go1.13.15:v1.0
命令: docker push <用户名>/<镜像名称>:<镜像版本号>
1 docker push fanhaodong/go1.13.15:v1.0
5、docker 其他命令 1、docker build docker build --build-arg arg=value --file Dockerfile_path --tag name:version build_path
1 2 3 4 5 FROM alpine:latestARG IMG_V=1.0 ENV IMG_V=${IMG_V}CMD [ "sh" ,"-c" ,"env" ]
执行:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 ➜ docker-file-test docker build --tag test:v1 --file ./Dockerfile --build-arg IMG_V=2.0 . Sending build context to Docker daemon 20.99kB Step 1/4 : FROM alpine:latest ---> a24bb4013296 Step 2/4 : ARG IMG_V=1.0 ---> Running in bd247961f4c5 Removing intermediate container bd247961f4c5 ---> 48608560ae13 Step 3/4 : ENV IMG_V=${IMG_V} ---> Running in 0ccb1c5aef84 Removing intermediate container 0ccb1c5aef84 ---> 45d309fc4a52 Step 4/4 : CMD [ "sh","-c","env" ] ---> Running in 6d266d8d8301 Removing intermediate container 6d266d8d8301 ---> d4ccf528c0ed Successfully built d4ccf528c0ed Successfully tagged test:v1 ➜ docker-file-test docker run --rm test:v1 HOSTNAME=59991997b9be SHLVL=1 HOME=/root IMG_V=2.0 PATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin PWD=/
可以看到成功 执行了环境变量!
2、docker run 传递env 1 2 FROM alpine:latesta CMD [ "sh","-c","env" ]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 [admin@centos-linux docker-file-test]$ docker build -t test-1 . Sending build context to Docker daemon 23.04kB Step 1/2 : FROM alpine:latest ---> a24bb4013296 Step 2/2 : CMD [ "sh","-c","env" ] ---> Running in 65c81ab9dc1f Removing intermediate container 65c81ab9dc1f ---> 027268ad86ee Successfully built 027268ad86ee Successfully tagged test-1:latest [admin@centos-linux docker-file-test]$ docker run --env demo=1 test-1 HOSTNAME=d4504e8ef3be SHLVL=1 HOME=/root PATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin demo=1 PWD=/
传递环境变量,是可以到运行时!
3、docker start shell脚本启动 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 # !/bin/bash # 获取cid CID=$(docker create --rm test-1) # 根据cid启动 docker start $CID # flag echo "start success!!!!"
运行
1 2 3 [admin@centos-linux docker-file-test]$ bash new.sh dd9159e2d3da614f6dc7f816300d75ad58c6acf673eb9bea1e8a3f3af60a4137 start success!!!!
good 启动了 !!!
5、挂载 docker run --rm -v /opt test-3
如果容器销毁,宿主机文件也会被销毁!!!!
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 "Mounts": [ { "Type": "volume", "Name": "79c49a14a84ce8f6ba852e11d91a109ac1c02a6649e83f68b316990404035148", "Source": "/var/lib/docker/volumes/79c49a14a84ce8f6ba852e11d91a109ac1c02a6649e83f68b316990404035148/_data",// 宿主机目录 "Destination": "/opt", // 容器目录 "Driver": "local", "Mode": "", "RW": true, "Propagation": "" } ], "Volumes": { "/home/admin/dong/docker/docker-file-test": {} },
docker run --rm -v /home/admin/dong/docker/docker-file-te/:/opt test-3
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 "Mounts": [ { "Type": "bind", "Source": "/home/admin/dong/docker/docker-file-test", "Destination": "/opt", "Mode": "", "RW": true, "Propagation": "rprivate" } ],
6、docker commit 这个比较适合不会写docker file的人,这里我举个例子,假如现在我们有一个centos:7
其次,我们要安装一个curl命令
1 2 3 4 ➜ /data docker run --rm -it 7e6257c9f8d8 /bin/bash [root@bcdaea8354a6 /]# yum install -y curl [root@bcdaea8354a6 /]# curl www.baidu.com <!DOCTYPE html> // good
此时我们只需要进行
1 2 3 4 5 ➜ ~ docker ps -a -l CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES bcdaea8354a6 7e6257c9f8d8 "/bin/bash" 2 minutes ago Up 2 minutes happy_liskov ➜ ~ docker commit bcdaea8354a6 demo-2 sha256:350fbf288cb1a47a29e3d8e441e2814726de6faf54d044a585fb80b7a1f38f83
这个镜像就OK了,就可以使用 demo-2的镜像了